Digital Transformation in Healthcare – Everything You Need to Know
The entire business world is going through a digital transformation. While organizations that were encouraged by the benefits offered by digital technologies embarked on this journey first, others were forced to move digital, owing to the pandemic that brought the unexpected lockdown. While the healthcare segment was slow to adopt digital technologies owing to the lack of expertise to decide on where to invest and how to invest, the recent trends reveal that healthcare institutions are now aggressively embracing digital transformation.
What is Digital Transformation in Healthcare?
 Digital transformation in healthcare is about implementing digital technologies to improve healthcare operations, increase patient experience while making healthcare cost-effective and accessible to everywhere, on-demand. Right from online appointments to managing EHRs and medicine reports to integrating various departments for seamless coordination, digital transformation makes healthcare services efficient, easy to use and accessible everywhere.
Digital transformation in healthcare is about implementing digital technologies to improve healthcare operations, increase patient experience while making healthcare cost-effective and accessible to everywhere, on-demand. Right from online appointments to managing EHRs and medicine reports to integrating various departments for seamless coordination, digital transformation makes healthcare services efficient, easy to use and accessible everywhere.
According to Global Market Insights, the global digital healthcare market was valued at $141.8 billion in 2020. This value is expected to grow at a CAGR of 17.4% between 2021 and 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research reports that the global healthcare market earned a revenue of $96.5 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.1% during the period 2021-2028. These numbers speak volumes of the growing popularity of digital transformation in recent times.
How Digital Transformation Helps Healthcare?
Digital transformation is not a silver bullet that can simply transform existing healthcare institutions. It requires proper planning and implementation. Organizations that have rightly implemented digital technologies are reaping the following benefits:
Centralized Data Management Systems
Gone are the days when patients had to wait in long queues to meet a doctor, undergo tests/scans and return to join the long queues for treatment. With digital technologies incorporated across the organization, patients can now schedule an appointment from the comfort of their homes and get treatment at their convenience. With a single digital ID, doctors can pull out the records of the patient and check out the illness history. Similarly, the diagnostics department staff can retrieve the patient details and update them with the test reports so that the doctor can prescribe the right medicine which is then passed on to the pharmacy wing. With a centralized data management system, concerned people across the healthcare can access the required patient information and deliver quality care. Patient care becomes quick, easy and accessible for everyone.
Patient Portals
A patient portal is an intuitive online healthcare platform that enables patients to access their medical records, communicate with healthcare professionals, receive telemedicine etc. It enables them to access the data from anywhere, any location on-demand and share the test reports and case histories with multiple healthcare providers, gaining better control over the treatment.
Virtual Treatment / Video Call
Today, patients don’t have to visit a healthcare professional for regular sicknesses. Instead, they can contact a medical practitioner via a video call and get their illness treated over the phone. Whether you are in the office, at home or on the road, it is a breeze to search for a healthcare professional and communicate with them on a video call. It is especially useful in rural areas wherein healthcare services are scarce. It means digital transformation extends healthcare to most rural parts of the country. Virtual treatment has helped several patients during the time of Covid. While these options don’t negate direct visitations, they help you in times of health emergencies.
Wearable Technology
Wearable medical devices are on the rise in recent times. With the help of wearable devices, patients can keep track of high-risk conditions and prevent a health upset. For instance, you can monitor heartbeats, sweat, pulse rate, oxygen levels etc. using a wearable device and instantly contact emergency support in case of an emergency. The device can automatically send alerts to your prescribed contacts in case of unusual health metrics. Not only does it prevent a health event but it also saves high medical expenses.
Healthcare / Wellness Apps
Using digital technologies, healthcare professionals can design healthcare or wellness apps that enable patients to track and manage their health from the comfort of their homes. For instance, you can use a wellness app to receive recommendations on food and nutrition. Similarly, you can get mental health counselling from trained and experienced professionals on-demand. There are beauty care apps that can help you to manage your skin for acne, allergy or other issues. Similarly, some apps track your sugar levels, eye health etc.
As healthcare is aggressively moving towards digital transformation, designing the right digital strategy with the right technology stack is the key to fully leveraging this revolution.
Contact CloudTern right now to embark on the digital transformation journey!
Top 10 Critical Questions You Should Ask While Choosing a Cloud Computing Provider
 Here is a popular joke about the increasing popularity of cloud computing technologies in recent times.
Here is a popular joke about the increasing popularity of cloud computing technologies in recent times.
Today, cloud computing has become so popular that almost every IT resource is being moved to the cloud and delivered over the Internet via a pay-per-use model.
However, cloud computing is not a silver bullet. You can’t just click a button to make everything cloud-enabled.
To fully leverage the cloud revolution, it is important to identify your cloud computing needs and design the right cloud strategy. Choosing the right cloud computing provider is the key here.
Here are the top 10 questions to ask your cloud computing provider before hiring one.
1) Services Portfolio
Before moving to the cloud, organizations should identify their cloud computing needs and document the requirements. Once you have this document ready, the first and foremost question to ask your cloud provider is about their portfolio offerings. What are the cloud services they offer? If they don’t offer the services required by your company, there is no point in further negotiations with the company. You can delete it and move with other companies in the list.
2) Subscription Models
Another important question to ask your cloud service provider is about how they charge for the services offered and how flexible is their payment structure. The cheapest services should not be the first choice. While the price is an important factor, align it with the services to make a decision. While most cloud services are normally offered via a pay-per-use model, the charges differ based on the instances, servers, users, groups, regions etc. In addition, check out the payment period – monthly, quarterly, annually etc.
3) Cloud Security
One of the main barriers to cloud adoption for many organizations is data security. As such, check out the security policies and cyber security measures implemented by the company. Multi-factor authenticating (MFA) is not an option anymore. So, check out if they offer a multi-factor authentication system? In addition, intrusion detection, data encryption, incident prevention mechanism, firewalls and visibility into network security are some of the key requirements to consider.
4) Data Storage Location

The location of the datacenter can affect the performance and reliability of your applications. Choosing a datacenter closer to your business operations will give you an added advantage. As such, ask the cloud provider about where they store your data and what security policies they have in place.
Does it have a fall-back center to handle natural and accidental disasters? Another reason to know the datacenter location is that companies are required to comply with data regulations of their regions. So, it is important to know the data storage location for audit and compliance purposes too.
5) Service-Level Agreements (SLAs)
Before subscribing to a cloud service provider, it is important to define your expectations related to their services. So, check out how they measure the services and how they compensate for service outages. Going through their SLA agreement will help you in this regard.
6) Flexibility in Services
One of the biggest advantages of cloud solutions is the flexibility it offers in adding or terminating services on-demand. So, check out with the provider if you can instantly add or modify services on the go and how easy it is to make changes to your services. For instance, short-term projects require short-term resources on-demand. It will help your team to experiment with new ideas. In addition, check out if you can scale up and scale out resources without downtimes. If an autoscaling feature is available, that would be great.
7) Customer Support 24/7
Regardless of how good a cloud company is, there will be times you might experience a service outage or other technical issues. In such instances, you need a support system that can instantly resolve your issue. So, check out with the cloud provider if they offer customer support that is available 24/7/365 as you need the support service on holidays and weekends as well. In addition, find out the available support options such as phone support, chatbot service, email etc.
8) The History of Downtimes
While no cloud company can guarantee 100% uptime, the best cloud provider should be able to quickly resolve technical issues and minimize downtimes. So, check out the downtime history of the company and what steps they have taken to get things back on track. You can also check out these details on their website and review sites to assess the availability of their services. You don’t want to join hands with a company that has frequent outages.
9) Data Control
While using a cloud service, the cloud provider takes care of the infrastructure while you focus on your business operations. However, it is important to know how the data is handled and what type of control you have over the data. Would you be able to retrieve all your data without the assistance of the provider in case you want to change the provider or terminate the services? In addition, it is important to know how long they will store the data after the service agreement comes to an end. What type of data formats are available is another aspect to check out.
10) Does the company make timely backups?
Data backup and recovery is key to safeguarding your business information. So, check out if the company performs timely backups so that you can restore a recent backup when the data is lost or erased. In addition, check out their disaster recovery plan. Do you have recovery measures in place to instantly recover data or prevent a disaster to happen? A cloud computing company without a DR plan cannot be trusted.
The cloud market is flooded with multiple cloud service providers. So, it is important to eliminate companies that are inefficient, incompatible and unreliable. In addition to asking the above questions, you need to check out the reputation of the company, their references, feedback on review sites and social media platforms etc. Taking time for these tasks will save your business from incurring huge losses in the long run.
Everything You Need to Know about 5G
5G is the new global wireless standard that has succeeded the 4G network. 5G, also called the 5th generation mobile network, is designed to bring devices, machines and objects into connectivity, delivering massive network capacity, high-speed, low latency and high availability networks. According to Grand View Research, the global 5G infrastructure was valued at $41.48 billion in 2020. This value is expected to grow at a CAGR of 46.2% between 2021 and 2028. ResearchandMarkets opines that the global 5G infrastructure market will touch $80.5 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 49.8% between 2021 and 2028.
The Evolution of 5G
The 1st generation network (1G) that was introduced in the 1980s used analog technology to provide mobile communications. It was succeeded by the 2nd generation network called 2G in the 1990s and used digital systems to offer voice data and SMS services. The 3rd generation mobile network 3G introduced GSM networks. The advent of 4G network revolutionized this space with LTE and LTE-Advanced capabilities for high-speed networks. The 5th generation network 5G takes it to the next level bringing New Radio (NR) and LTE-Advance Pro technologies into foray to facilitate ultra-low latency and high-speed networks.
 5G is not developed by a single company but receives contributions from multiple companies in the form of foundational technologies and global specifications. The 5G ecosystem includes mobile network operators, infrastructure vendors, device manufacturers etc. 3rd Generation Partner Project (3GPP) is an important organization that is instrumental in designing the service layer, air interface and global specifications for 5G.
5G is not developed by a single company but receives contributions from multiple companies in the form of foundational technologies and global specifications. The 5G ecosystem includes mobile network operators, infrastructure vendors, device manufacturers etc. 3rd Generation Partner Project (3GPP) is an important organization that is instrumental in designing the service layer, air interface and global specifications for 5G.
The 5G technology uses the Orthogonal Frequency-division Multiplexing technology that divides signals across multiple channels to minimize interference. New Radio (NR) is another underlying technology of 5G that enhances OFDM principles to bring high scalability and flexibility to network operations. 5G operates across millimetre wave (mmWave) high-band, low-band and mid-band, delivering speeds between 4 Gbps and 20 Gbps. With high speeds and low latency, 5G supports mission-critical communications and massive IoT networks.
Benefits of 5G
5G offers amazing benefits for organizations and individuals. The high-speed network enables you to download an HD movie on your mobile in seconds. During a sporting event in a stadium, 5G facilitates reliable connectivity for thousands of concurrent users. Sports broadcasting becomes easy and efficient as well. Sports clubs are now planning to deliver game insights in real-time to enhance user experience. For sports clubs, it facilitates better crowd management. Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies take advantage of 5G to deliver an immersive experience in games, apps as well as in virtual meetings.
The ultra-low latency of 5G enables authorities to build safe and sustainable smart cities with autonomous vehicle systems and intelligent traffic management systems. Thousands of vehicles can communicate with each other and share data to reduce accidents. Emergency services can be deployed faster too. Natural disasters can be quickly detected using sensors.
5G brings innovation into industrial production as well. It helps companies in securely combining people and robots to smartly work together without getting cobbled with cords and machines. Businesses can run predictive and prescriptive analytics in real-time. With IoT networks, businesses can monitor and improve performance, production and logistics.
There has been a buzz around the negative impact of 5G on the environment which turns out to be far from true. 5G technology is safe and sustainable and businesses are already embracing it to surge ahead of the competition.
Is your business 5G-ready? Contact CloudTern right now to leverage this amazing revolution!
5G Applications and Use Cases
The buzz around the introduction of 5G technology, its pros and cons and the effect on the environment has finally taken the backstage as businesses are now slowly deploying 5G networks across the globe. According to MarketsandResearch, the 5G market is expected to touch $80.5 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 49.8% during 2021 and 2028. As 5G deployments are increasing, the technology is expanding into various verticals.
5G applications and use cases can be broadly classified into three categories:
1) Machine type communications / IoT Use Cases
 The 5G technology has significantly augmented IoT networks. Leveraging the speed, reliability and coverage, businesses are now able to set up operations in remote locations while being able to sync with central systems in real-time. For instance, 5G facilitates smart factories wherein robots and humans work together in a wireless environment, eliminating cords and cables that hamper the speed and smoothness of operations. In addition, 5G provides the required range and mobility while significantly improving the quality of service.
The 5G technology has significantly augmented IoT networks. Leveraging the speed, reliability and coverage, businesses are now able to set up operations in remote locations while being able to sync with central systems in real-time. For instance, 5G facilitates smart factories wherein robots and humans work together in a wireless environment, eliminating cords and cables that hamper the speed and smoothness of operations. In addition, 5G provides the required range and mobility while significantly improving the quality of service.
With the implementation of Augmented Reality / Virtual Reality (AR/VR) technologies, businesses enable workers to interactively operate complex machinery. In the sporting environment, AR/VR offers an immersive experience with its high speed and low latency. When it comes to delivering goods, companies like Amazon have already started using drones. The 5G technology enables companies to extend operations to remote locations with good quality of service.
The wearable technology segment hugely benefits from 5G. In today’s technology world, every household uses a myriad of gadgets, right from mobiles, tablets and laptops to wearables and trackers. The traditional cellular network won’t be able to deliver a comprehensive and connected experience. With 5G, all your devices can be connected to the network and can talk to each other in real-time.
2) High-Speed Mobile Broadband Use Cases
When it comes to streaming content on mobile devices, the introduction of 4G has significantly improved the customer experience. However, it only facilitated SD quality and HD to some extent. As the MPEG AVC codec is 1.5 M/s, 4G served the purpose. However, 5G brings 4K and 8K HD streaming into the picture, making it easy to stream high-quality bandwidth-intensive content to multiple users at the same time. While the mid-band deployments deliver up to 200 Mbps which is ten times the speed offered by 4G, high-frequency bands deliver connectivity of 1 Gbps. So, you can scale UHD video delivery. As of now, scaling video for live mobile applications is a challenge. With 5G, this option is expected to become a reality in 2-3 years.
3) Low Latency Use Cases
When it comes to running applications that demand low latency, 5G offers a good bet. For instance, smart city infrastructure is being implemented in many cities wherein vehicles are connected via a smart transport system and can communicate with other vehicles as well as with the infrastructure. With 5G implemented in this system, communication becomes effective and reliable.
Similarly, autonomous vehicle technology is a new trend that is quickly catching up. Machine learning, real-time data communication and network speed are key requirements for this system and vehicles should be able to communicate with the system in real-time, learn through live data and make decisions accordingly, 5G helps here as the connectivity speed increases by 10-100 times. As such, vehicles can instantly send information and receive instructions within milliseconds and quickly respond to changes happening around them. This difference in latency can make a difference in life and death. Similarly, edge computing networks become efficient and reliable as systems can quickly process more data without the need to access centralized systems that are located miles away.
As 5G technology takes the center stage, more and more applications are benefitting from the high speed, low latency and mobility solutions offered by the network. The advent of 5G is already disrupting the technology space. Businesses that take advantage of this trend at the earliest are sure to surge ahead.
Top 10 Myths about DevOps Development
DevOps was introduced between 2007 and 2008 as a revolutionary methodology that would be disrupting the IT development landscape. While DevOps was successful in changing the way how IT thinks and operates, it took a long time for companies to adopt this methodology. The reason for this slow adoption was because businesses took time to understand how DevOps works. While organizations are aggressively embracing this methodology in recent times, there are still some misconceptions that are acting as a barrier to DevOps implementation. Here are the top 10 myths about DevOps development.
1) DevOps is a Tool
The most popular myth about DevOps is that it is a tool or a product which is not true. DevOps is not a tool or a technology that can be purchased or subscribed to. It is a methodology that integrates development, operations, QA and security teams into a cross-functional team to seamlessly collaborate and work on software development projects. The system uses tools, processes and people to achieve this. For instance, continuous integration is achieved using CI servers such as Bamboo, Jenkins, Gitlab etc. while Docker and Kubernetes help in automatic deployment and management of the infrastructure.
2) DevOps is for the Web
DevOps became popular with SaaS-based organizations such as Netflix and Etsy creating an impression that DevOps is only for web companies. While it is true that DevOps favours web platforms, it is equally effective for all types of modern software delivery. While continuous delivery helps web companies to always offer up-to-date software, the same applies to native and non-web software too.
3) DevOps means CI/CD
While DevOps helps organizations achieve continuous delivery by building CI/CD pipelines, it is only a part of the DevOps methodology. DevOps is not confined to CI/CD but deals with the organization more comprehensively. In addition to tools and processes, DevOps brings a cultural shift across the organization by creating cross-functional teams that seamlessly collaborate and communicate across the product lifecycle. To fully leverage DevOps, businesses should equally focus on people, tools and processes.
4) DevOps Solves all Problems
It is a common misconception that when you use DevOps to build continuous delivery pipelines and automate processes, the system will take care of everything without any issues. First of all, you need to design the right DevOps strategy with the right tools for the right processes that are managed by the right people. In addition, to automating processes, you need to set up continuous feedback loops, analyse metrics and constantly update things. DevOps is not a magic wand that automatically sets everything right.
5) DevOps is for Developers and Operations Teams
DevOps stands for Development and Operations. While it started off a system that integrated these two teams to collaboratively work on a software development project, it has greatly evolved now. Today, DevOps cross-functional teams include people from QA, security, administrators, data engineers, analytics engineers and business management. It is interesting to note that members from sales, marketing, and tech support and customer service are also being incorporated into cross-functional teams as and where applicable.
6) DevOps is the End of Operations Teams
In an automated DevOps environment, developers can automatically deploy software to production environments using tools such as Jenkins, TeamCity, Docker, Kubernetes etc. However, it doesn’t mean that it is the end of the road for operations professionals. Actually, Ops teams can take advantage of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools to efficiently manage the infrastructure via code. DevOps teams are accountable for the entire lifecycle of the product and Ops teams have an important role to play here.
7) Operations Professionals Should Learn Programming
With infrastructure as code taking the center stage of the infrastructure management landscape, there is a misconception that operations professionals should learn programming languages. While it is true that you need a basic idea of scripting, you don’t need to have expert knowledge of programming languages such as Java or C#. For instance, Ruby is a popular IaC language that is easy to learn. So, Ops teams with basic scripting knowledge can easily pick up this system.
8) DevOps is only for Non-Regulated Industries
Often, people think that DevOps doesn’t work well with highly regulated industries, owing to strict compliance and security policies. DevOps serves a great purpose for regulated industries as well. With DevOps, compliance becomes easy as you can store audit trails of all automated processes. It means business processes are always audit-ready.
9) DevOps is Cloud-based
Often, people believe that DevOps is always deployed in the cloud and some people use the term ‘cloud’ interchangeably with DevOps. DevOps indeed brings dynamic infrastructure resources into the picture. However, it doesn’t mean that DevOps always requires a cloud infrastructure. If you can dynamically test and deploy code, then DevOps works for you.
10) DevOps replaces Agile
A popular myth about DevOps is that it replaces agile which is not true. In fact, DevOps enables agile practices by incorporating continuous integration, continuous testing, continuous deployment and continuous monitoring. So, it actually complements agile software development.
The key to fully leveraging DevOps is choosing the right DevOps strategy. CloudTern is here to help!
DevOps for Business Intelligence
DevOps started off as a methodology that integrates Developers and Operations teams to work in tandem in software development projects. It facilitates seamless coordination and communication between teams, reduces time from idea to market and significantly improves operational efficiencies while optimizing costs. Today, DevOps has rapidly evolved to include several other entities of IT systems. A new addition is Business intelligence.
DevOps jelled well with Big Data as both methodologies are contemporary and complement each other in managing of massive volumes of live data moving between development and production that is maintained relevant via seamless coordination between teams. When it comes to business intelligence, data warehousing and analytics are two important components that need to be managed. As BI deals with batches of data, it doesn’t easily integrate with the DevOps environment by default.
Managing Data Warehousing with DevOps
A data warehouse is a central data repository that collects data from various disparate data sources in and outside the organization and hosts them in a central location allowing authorized people and reporting and analytics tools to access it from any location. Managing a robust and sophisticated data warehouse is a challenge as multiple stakeholders are involved in making a change which makes deployments rather slow and time-consuming. Implementing DevOps here can be a revolutionary thing as you can combine data administration teams and data engineering teams to collaborate on data projects. While a data engineer informs potential features that are being introduced to the system, the data administrator can envisage production challenges and make changes accordingly. With cross-functional teams and automated testing in place, production issues can be eliminated. Together, they can build a powerful automation pipeline that comprises data source analysis, testing, documentation, deployment etc.
However, introducing DevOps for data warehouse management is not a cakewalk. For instance, you cannot simply backup data and revert to the backup as and when required. When you revert to a last week’s backup, what about the changes made to the data by several applications?
DevOps for Analytics
The analytics industry is going through a transformation as well. Contrary to the traditional analytics environment that uses a single business intelligence solution for all IT needs, modern businesses implement multiple BI tools for different analytical purposes. The complexity is that all these BI tools share data between them and there is no central management of BI tools. Another issue is that data scientists design models and algorithms for specific data sets to gain deeper insights and offer predictions. However, when these data sets are deployed to the production environment, they serve a temporary purpose. As data sets outgrow, they become irrelevant which means continuous monitoring and improvement is required. The rate at which the data drifting happens is enormous and traditional analytics solutions are inefficient to manage this speed and diversity. This is where DevOps comes to the rescue.
DevOps helps businesses integrate data flow designs and operations to automate and monitor data enabling them to deliver better applications faster. Automation enables organizations to build high performing and reliable build-deploy iterative data pipelines for improving data quality, accelerate delivery and reduce labor and operational costs. Monitoring data for health, speed and consumption-ready status enable organizations to reduce blindness and eliminate performance issues. It means a reliable feedback loop is created that covers data health, privacy and data delivery for ensuring smooth flow of operations for planned as well as unexpected changes.
The Bottom Line
Bringing DevOps into the BI realm is not an easy task as BI environments are not suitably designed for DevOps. However, businesses are now exploring this option. Bringing DevOps into the BI segment gives situational awareness to businesses as they can make informed decisions when they gain insights into relevant data added from multiple sources. Moreover, it brings great collaboration between teams, allows better integration between different application layers while helping businesses to explore and quickly tap into new markets. Most importantly, it makes your business future-proof.
Top 5 Advantages of using Docker
 As businesses are aggressively moving workloads to cloud environments, containerization is turning out to be a necessity for every business in recent times.
As businesses are aggressively moving workloads to cloud environments, containerization is turning out to be a necessity for every business in recent times.
Containerization enables organizations to virtualize the operating system and deploy applications in isolated spaces called containers packed with all libraries, dependencies, configuration files etc.
The container market is rapidly evolving. According to MarketsandMarkets, the global application containerization market earned a revenue of $1.2 billion in 2018 and is expected to touch $4.98 billion by 2023, growing at a CAGR of 32.9% during 2018 and 2023.
The Dominance of Docker
The containerization market is dominated by Docker. In fact, it was Docker that made the containerization concept popular. According to Docker, the company hosts 7 million+ applications with 13 billion+ monthly image downloads and 11 million+ developers involved in the process. Adobe, Netflix, PayPal, Splunk, Verizon are some of the enterprises that use Docker.
Virtual Machine Vs Docker
Here are the top 5 benefits of using Docker:
1) Consistent Environment
Consistency is a key benefit of Docker wherein developers run an application in a consistent environment right from design and development to production and maintenance. As such, the application behaves the same way in different environments, eliminating production issues. With predictable environments in place, your developers spend more time on introducing quality features to the application instead of debugging errors and resolving configuration/compatibility issues.
2) Speed and Agility
Speed and agility is another key benefit of Docker. It allows you to instantly create containers for every process and deploy them in seconds. As you don’t have to boot the OS, the process is done lightning fast. Moreover, you can instantly create, destroy, stop or start a container with ease. By simply creating a configuration file using YAML, you can automate deployment and scale the infrastructure at ease.
Docker increases the speed and efficiency of your CI/CD pipeline as you can create a container image and use it across the pipeline while running non-dependant tasks in parallel. It brings faster time to market and increases productivity as well. The ability to commit changes and version-control Docker images enable you to instantly roll back to an earlier version in case a new change breaks the environment.
3) Efficiently Management of Multi-Cloud Environments
Multi-cloud environments are gaining popularity in recent times. In a multi-cloud environment, each cloud comes with different configurations, policies and processes and are managed using different infrastructure management tools. However, Docker containers can be moved across any environment. For instance, you can run a container in an AWS EC2 instance and then seamlessly move it to a Google Cloud Platform environment with ease. However, keep in mind that data inside the container is permanently destroyed once the container is destroyed. So, ensure that you back up the required data.
4) Security
Docker environments are highly secure. Applications that are running in Docker containers are isolated from each other wherein one container cannot check the processes running in another container. Similarly, each container possesses its own resources and doesn’t interact with the resources of other containers. They use the resources allocated to them. As such, you gain more control over the traffic flow. When the application reaches its end of life, you can simply delete its container, making a clean app removal.
5) Optimized Costs
While features and performance are key considerations of any IT product, Return on Investment (ROI) cannot be ignored. The good thing with Docker is that it enables you to significantly reduce infrastructure costs. Right from employee strength to server costs, Docker enables you to run applications at minimal costs when compared with VMs and other technologies. With smaller engineering teams and reduced infrastructure costs, you can significantly save on operational costs and increase your ROI.
How Kubernetes Helps in Transforming your Business?
Today, the majority of businesses are going through a digital transformation. While the digital journey brings speed, efficiency and mobility solutions to the table, it comes with certain challenges too. As you migrate the existing infrastructure to the cloud, you’ll have to deal with legacy issues. In the cloud, you have to manage a wide range of tools and services. The implementation of DevOps to manage your infrastructure gives you additional responsibilities.
 The DevOps environment demands frequent and faster deployments every day. According to the State of the DevOps 2019 report, elite performers make 209 times more deployments than low performers.
The DevOps environment demands frequent and faster deployments every day. According to the State of the DevOps 2019 report, elite performers make 209 times more deployments than low performers.
They gain 106 times faster lead time from commit to deploy with a 7% change fail rate. The time to recover from incidents is 2,604 times faster than low performers.
Gone are the days when IT development was confined to software companies. Today, every enterprise develops and manages a wide range of software applications.
As such, tracking and managing automated deployments is a challenge. Kubernetes is here to help.
An Overview of Kubernetes
Kubernetes is a popular tool that enables administrators to orchestrate and manage server cluster workloads in a datacenter, including automation and declarative configuration. Also known as K8s, the Kubernetes open-source platform helps you in efficiently managing containerized apps and services. You can simultaneously run and manage multiple servers while providing access to resources 24/7. This is achieved with the implementation of distributed data processing that allows Kubernetes to run multiple servers of different kinds installed at different locations and operating on different platforms.
The Traditional Software Development Environment
In a traditional operations environment, multiple applications are hosted on a single physical server. It resulted in an inefficient allocation of resources as some applications consumed more resources while others were left out to underperform. Installing each application on a separate server consumed huge infrastructure expenses. Moreover, each server was underutilized. Virtual machines came as a solution to this issue. A virtual machine runs the operating system on top of the virtual hardware and contains all the required elements to run the applications. Using virtualization, administrators were able to isolate applications between different VMs and run multiple applications on the same physical machine.
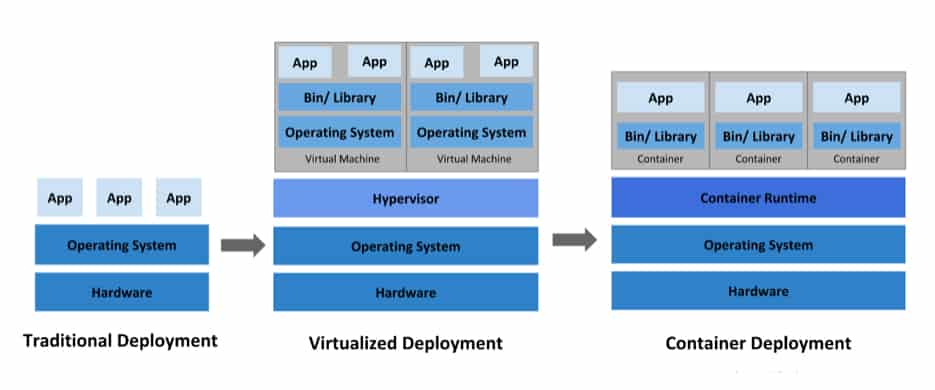
The Advent of Containerization
The container technology takes this system to a next level. A container is a software package that is bundled with all the required components of the app such as binaries, dependencies, libraries and configuration files while isolating it from the underlying hardware. Containers are lightweight and enable administrators to seamlessly deploy workloads across multiple environments. Keeping the base image consistent, developers can run the app in any environment. By sharing the host OS, containers eliminate the need for libraries and boot OS and therefore become lightweight. They are highly scalable, highly portable, offer agility and provide application-centric management.
Today, enterprises simultaneously run hundreds of containers in different environments. As such, managing the deployment of containers, tracking each container and setting up a new container when a container is down is a challenge. Kubernetes helps you to define your deployment patterns and efficiently manage resilience in a distributed systems environment.
Kubernetes and Containerization
Kubernetes is the most popular container-deployment system for the following reasons. Firstly, it enables you to provide access to containers via an IP address or a DNS name. In addition to service discovery, it helps you to perform load balancing for routing traffic to the right container. Secondly, infrastructure management becomes easy as you can define the desired state of a container. At any given point in time, you can easily roll back the system to its desired state and create and terminate containers at your will. It supports self-healing wherein containers are automatically replaced or restarted. Be it local storage or a public cloud datacenter, Kubernetes allows you to mount storage automatically for efficient orchestration of storage.
While managing a cluster of servers, you can define resource allocation (RAM, CPU) for each container and Kubernetes will optimize the infrastructure by rightly fitting containers onto the nodes. It also allows you to securely store and manage secret information such as passwords, keys etc. without exposing them in the configuration of the stack.
What is it for Businesses?
Powered by Cloud Native Cloud Foundation (CNCF), Kubernetes is the fastest-growing open-source software which means you are entitled to use a wide range of open-source tools developed for Kubernetes. Portability is a big benefit of Kubernetes. It means you not only manage the automatic deployment of large clusters of servers but also moves them between multi-cloud environments with ease.
Kubernetes offers high scalability enabling you to run containers or different environments such as a virtual machine, public, cloud, bare metal. Organizations enjoy high availability at the infrastructure level as well as the application level. You can configure it to support multi-node replication or add a storage layer for the high availability of stateful workloads. Kubernetes uses a simple client-server architecture but offers amazing benefits such as auto-scaling, rolling updates, self-healing etc. Backed by Google, you can rest assured of its reliability and credibility.
Businesses hugely benefit from faster time to market, increased productivity, high availability, high scalability, IT cost optimization, seamless migration between multi-cloud environments and many more. Most importantly, it makes your business future-proof.
Are you leveraging the benefits of Kubernetes? If not, CloudTern is here to help!
Top 10 Benefits of AWS in 2021
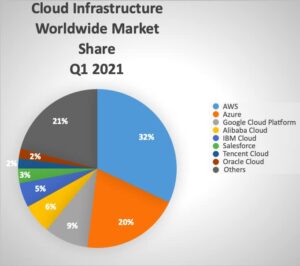 Technology is changing rapidly every year. The year 2021 is no different. However, one thing that remains constant here is the position of AWS in the public cloud infrastructure segment. AWS has been a leader in this segment since its advent.
Technology is changing rapidly every year. The year 2021 is no different. However, one thing that remains constant here is the position of AWS in the public cloud infrastructure segment. AWS has been a leader in this segment since its advent.
According to Statista, AWS accounted for a market share of 32% in Q1 2021 earning revenues of $39 billion which is a 37% increase from Q1 2020. Azure and Google Cloud Platform recorded a market share of 20% and 9% respectively.
Here are the top 10 benefits offered by AWS in 2021:
1) Access to a World-class Technology Stack
Not every business has the luxury of laying hands on a world-class technology stack, owing to budget constraints and the lack of expert staff. Thanks to the AWS cloud, today, even small and medium businesses have access to cutting-edge technologies. It brings all players onto the same platform creating equal opportunities for everyone. Now, small and medium businesses can compete with enterprise solutions.
2) Always Innovating
Innovation is a key component of AWS offerings. The AWS team is committed to constantly driving innovation into the cloud infrastructure offering. This is one of the main reasons why top brands use AWS. Though Azure and GCP can compete with AWS in the pricing structure, innovation is what keeps AWS two steps away from its competitors. Being an AWS customer, you’re assured of cutting-edge technologies at cost-effective prices.
3) Always Economic
While AWS offers cutting-edge technologies, it manages to maintain an affordable pricing structure. As you only pay for the resources consumed without making any upfront commitments or long-term contracts, costs are predictable and economic as well. You can visit the AWS Economics Center to know about how organizations are optimizing resources and saving costs. According to a Cloud Value Benchmarking study, on average, businesses have saved 27.4% reduction per user, 57.9% increase in VM managed per user, 37.1% decrease in time to market new features and 56.7% decrease in downtime. All these aspects add up to your savings. AWS offers a calculator to keep track of all your cloud expenses.
4) Highly Flexible
One of the biggest advantages of AWS is its flexibility which allows you to customize your technology stack. Be it a programming language, operating system, database or web application platform, you can pick and choose your stack and easily load them into the virtual environment offered by AWS. Similarly, you can choose an out-of-box platform or customize and configure the entire stack from scratch.
5) Easy to Use
AWS solutions are designed with ease of use in mind. Whether you are a novice user or a technology expert, AWS makes it easy to move your applications to the cloud. You can take advantage of the AWS console to access the web application platform. Alternatively, you can use the web services APIs to do so. AWS offers extensive documentation on how to use these web services APIs making your job easy and fast.
6) Security at its Best
Security and better control over the datacenter were the two important barriers to cloud adoption for a long time. However, AWS takes security pretty seriously. AWS security is based on a shared model wherein AWS controls the security on the cloud infrastructure while the customer handles security at the customer endpoint. Data is distributed across multiple datacenters making it resilient, faster to access and quick to recover from a disaster. All datacenters are secured with end-to-end protection. The company uses firewalls to ensure data is protected and encrypted while moving across endpoints. It offers the Identity and Access Management feature wherein users are provided with role-based access controls. Multi-factor authentication is available too.
7) Scale at your Pace
Taking advantage of the massive infrastructure and the pay-per-use model, you can start small and scale at your own pace. AWS offers Elastic Load Balancing and Auto Scaling features that enable you to automatically scale resources as per traffic surges. Automation of Horizontal scaling comes out of the box. For automating vertical scaling, you need to configure AWS Ops Automator V2.
8) Comprehensive Cloud Solutions
With AWS, you don’t have to look in other directions. AWS is a single-stop solution for all your cloud infrastructure needs. It offers a wide range of tools and services. With datacenters located in 190 countries, you can scale globally. In addition to its massive infrastructure, AWS has a wide partner network that helps you with required tools for every cloud need, right from migrating to the cloud and developing in the cloud to optimizing cloud operations and managing workloads.
9) Extensive Support
While AWS solutions are easy to use, the company offers extensive documentation and support when it comes to walking you through the installation or configuration of tools and services. AWS website contains documentation, user guides, videos, forums and blogs to help you with the stuff. You can take advantage of the vibrant community as well.
10) The Brand Matters
Along with all the above mentioned, the brand value matters too. AWS is the leader in the cloud infrastructure segment and delivers cutting-edge solutions. When you subscribe to AWS solutions, it means your business operations are powered by world-class technologies that are second to none. So, it gives a big boost to your operational efficiencies and increases trust among customers.
How DevOps helps your Company to Grow?
When DevOps arrived onto the technology platform, industry experts opined that it is going to revolutionize the IT world. However, businesses were slow to embrace this methodology. The reason was that many businesses could not understand what DevOps is actually about. As it is not a tool or a technology, people derive their own definitions, processes and methods. DevOps is a methodology that integrates Development and Operations teams to work as a single entity right through the product lifecycle to deliver quality software faster. According to Research Dive, the global DevOps market was valued at $4.46 billion in 2020. This value is expected to reach $23.36 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 22.9% during 2020-2027.
Here is how DevOps helps your company to grow:
Redefining Organizational Culture
While DevOps started off as a combination of development and operations teams, it has now evolved to include everyone involved in the product lifecycle. DevOps brings cross-functional teams into the picture comprising people from design, development, QA, operations, security etc. It facilitates seamless collaboration and trust between teams, breaking silos. With rightly aligned priorities and shared goals, every member of the team gains clear visibility into the progress of the project, resulting in a quality product delivered in time. It gives you better control over tools, processes and projects.
Redefining Technical Processes
Faster time to market is a key requirement to stay in the competition in today’s fast-paced world. However, speed shouldn’t kill the quality. DevOps allows you to deliver faster while not compromising on quality. Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) is a notable feature of DevOps.
In a traditional waterfall software development model, developers write the code first which is then sent to the testing team. If there are errors, the code is returned to developers for corrections. When the code successfully passes the test, it is sent to the staging environment and then deployed to production. To deliver an update, the product has to go through the entire process again.
With the advent of Microservices and agile methodologies, developers started developing the software as modular independent services in smaller and incremental cycles. DevOps helps businesses to manage microservices, SOA and agile environments in a better way. It integrates different disparate systems to work as a cohesive unit. It allows you to build a CI/CD pipeline and automate the entire process.
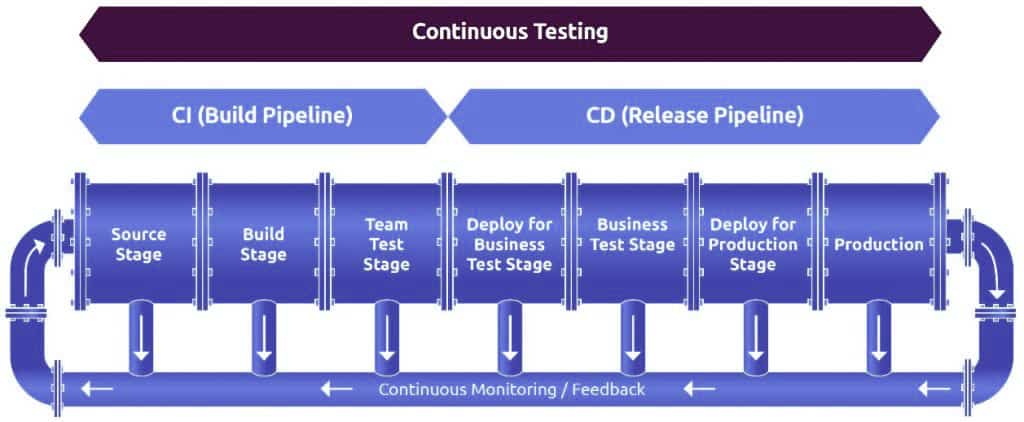
In this CI/CD pipeline, coders write the code and commit it to a version control system that acts as a central repository. When a change is detected, the CI server automatically runs the builds. Passed builds are moved to the deployment segment or the image repository. The automation deployment tool picks the artifacts from there are deploys them to production. There is a continuous monitoring tool that offers feedback from which you can gain clear insights into the performance of the product. By using value stream mapping, you can quickly identify bottlenecks and optimize every process. Response times get quicker too. With continuous integration, continuous testing, continuous deployment and continuous feedback, DevOps enables you to quickly deliver quality software.
Jenkins, Gitlab, CircleCI, TeamCity and Bamboo are some of the best CI tools that help you to automate and orchestrate the entire software development product lifecycle.
Redefining Business Processes
DevOps brings a cultural shift across the organization. Now, developers understand the challenges faced by the Ops guys and develop the code accordingly. Similarly, operations guys are aware of how the code is being developed and how it performs in production at an early stage. As each member is responsible for the overall quality of the product, every team equally cares for the efficient execution of tasks of other teams. They motivate and encourage other members wherever possible. With a cross-functional team working together, employees are cross-trained and up-skilled as well. It not only brings more value to the organization but also delivers more value to your customers.
Innovation is a key requirement to stay ahead of the competition. DevOps gives developers extra time to experiment and create new products or tweak existing products. With automated testing and automated security built into the pipeline, you don’t have to worry about breaking anything. Without disrupting the project, developers can validate the feasibility of ideas and introduce innovation into business processes. It also helps them learn customer requirements and user experiences in a better way and meet/exceed their expectations. Enhanced customer satisfaction helps you retain your customers and gain new referrals too.
The Bottom Line
DevOps benefits are equally distributed across the business, technical or cultural segments of an organization. A good DevOps strategy helps an organization sustainably grow in all aspects of the business. However, streamlining an end-to-end delivery pipeline is a challenge. Once the right DevOps strategy is designed, you can fully leverage all these benefits.
The key here is choosing the right DevOps partner!













